FMCG Brands Driving Sustainability with Regenerative Agriculture

Our food system is at a crossroads. Consumers are increasingly demanding transparency and sustainability, while the environmental impact of conventional agriculture is a growing concern. In response, a new wave of collaboration is emerging between major Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) brands and the Sustainable Agriculture Institute (SAI). This partnership focuses on a global standard for regenerative agriculture, offering a glimpse into a future where our food choices positively impact the planet.
Regenerative agriculture – an overview
Regenerative agriculture goes beyond damage limitation. It actively improves soil health, biodiversity, and water cycles. Practices like cover cropping, reduced tillage, and integrating livestock can help capture carbon, improve drought resilience, and create healthier ecosystems. The SAI Platform on Regenerative Agriculture provides a framework for brands and farmers to implement these practices and measure their impact.
Public commitments to regenerative agriculture
So, how are FMCG brands putting these principles into action? Many are making public commitments to source ingredients grown using regenerative methods. Unilever, for example, aims to have all its tea sourced regeneratively by 2025. Similarly, Kellogg’s has pledged to transition its entire wheat supply chain to regenerative agriculture by 2030. These commitments are significant, not just for the environmental benefits, but also for the message they send.

Image credit: Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership (CISL)
For consumers, these public commitments offer a level of transparency often missing in the food supply chain. By knowing where their food comes from and how it’s grown, consumers can feel empowered to make choices that align with their values. This transparency can also drive further innovation. As more consumers seek out regeneratively-grown products, it incentivises other brands to invest in sustainable practices.
The collaboration with the SAI is crucial for this movement’s success. The institute provides a global framework that ensures all stakeholders – brands, farmers, and consumers – are on the same page. This shared understanding allows for consistent measurement of progress and impact. Additionally, the SAI connects brands with farmers who are already implementing regenerative practices; facilitating partnerships and knowledge sharing.
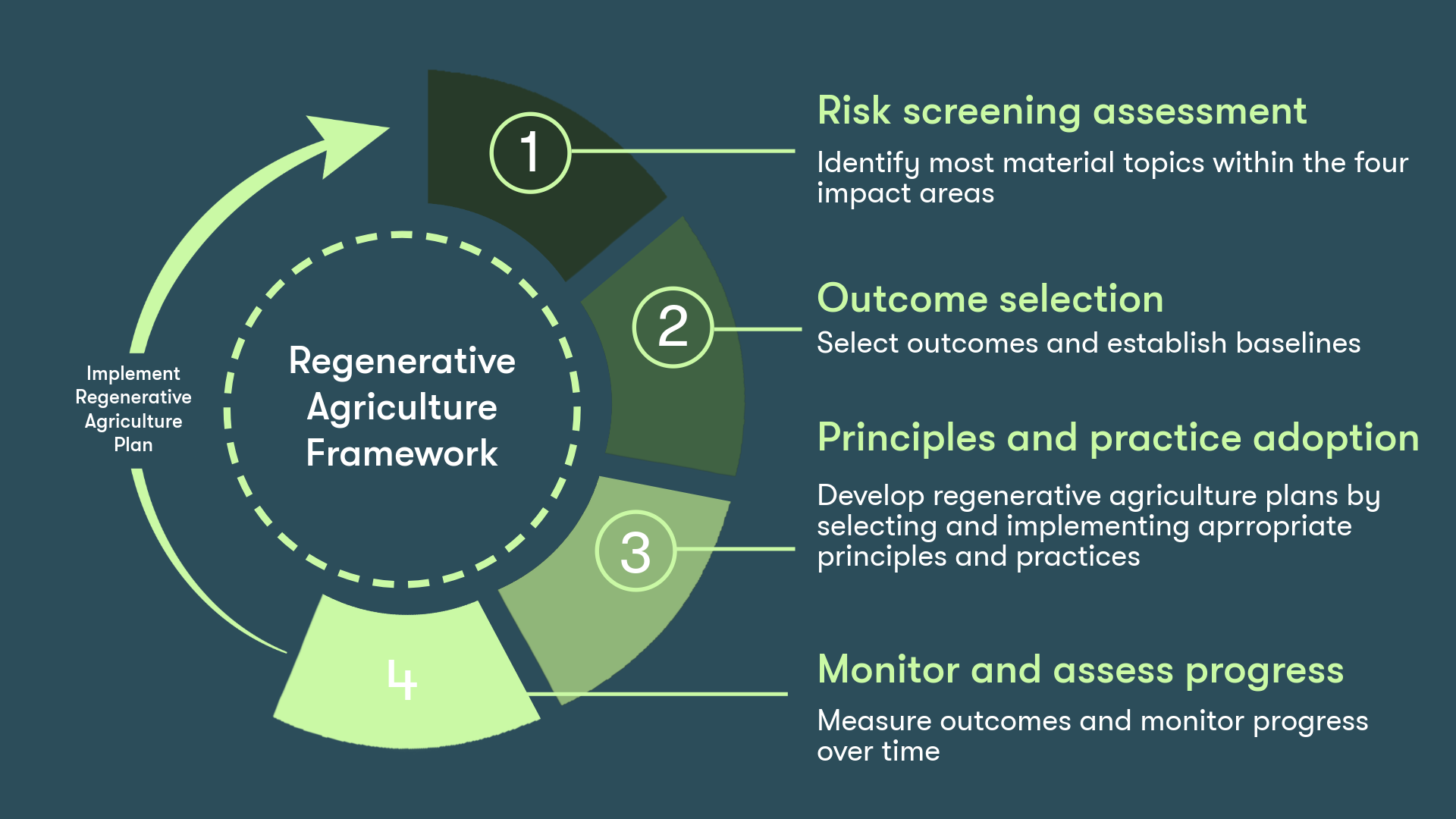
The process to implementing SAI Platform’s Regenerating Together standardised framework for regenerative agriculture
Challenges
Of course, there are challenges to overcome. Transitioning to new agricultural methods takes time and resources. Farmers need support in terms of training, access to funding, and technical assistance. FMCG brands are starting to address this by providing educational resources and financial incentives for farmers to adopt regenerative practices.
Summary
The movement towards regenerative agriculture is a positive step towards a more sustainable food system. By working together, FMCG brands, the SAI, and farmers can create a future where our food choices not only nourish us, but also heal the planet. This collaborative effort not only benefits the environment but also empowers consumers and fosters a more transparent food supply chain. As more brands embrace these practices, the seeds of positive change are being sown, paving the way for a healthier future for all.
In this article...



